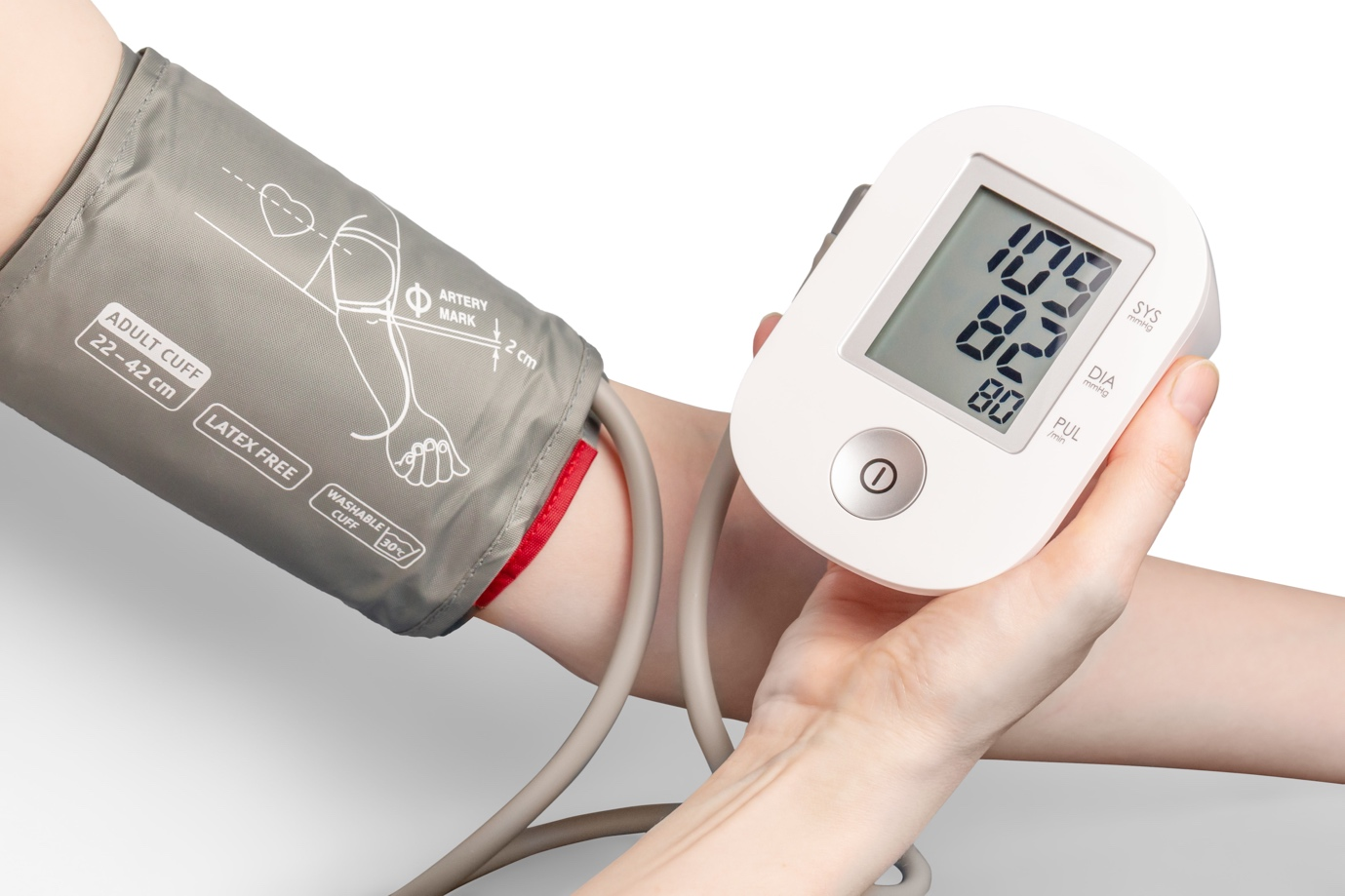
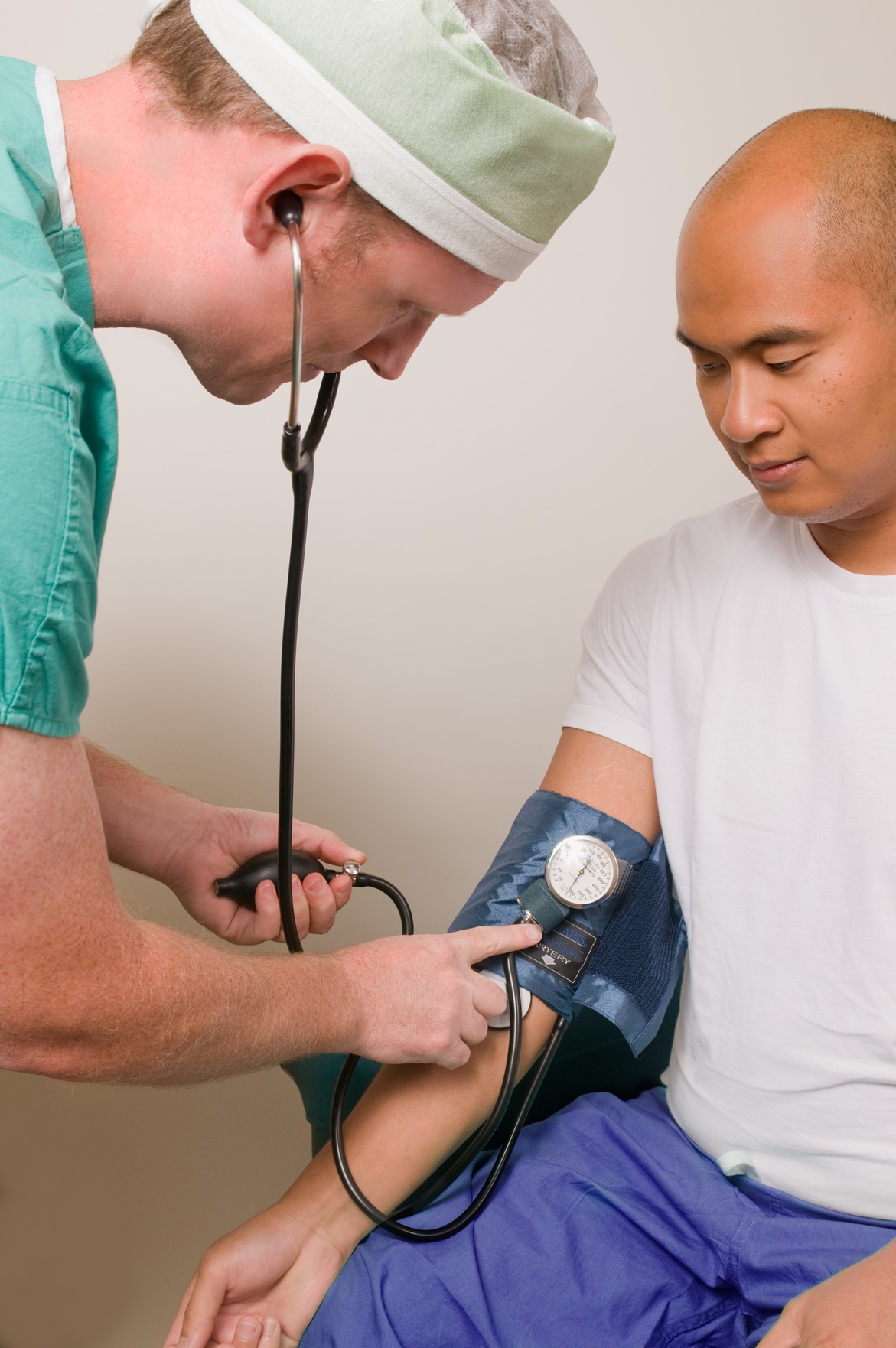
Blood Pressure
The force that blood exerts on the walls of the arteries as it is pushed throughout the body is known as blood pressure.
A person’s arteries are constructed to withstand some pressure, but there is a limit to what they can handle.That’s why blood pressure is monitored and categorized according to the impact it has on our health. The four types of blood pressure are:
- Lower than 120/80 mmHg – normal blood pressure.
- Readings of 120-129/80 mmHg – high blood pressure.
- Reading of 130-139/80-90 mmHg – Stage 1 hypertension
- Readings of 140/90 mmHg or greater – Stage 2 hypertension
Only blood pressure that is within normal limits is considered healthy. Blood pressure that is too high or too low harms your heart and arteries by increasing the rate at which your heart beats. This causes the heart muscle to thicken over time, making it more difficult for the heart to fill with blood and pump it. It also makes your arteries narrow and harden up. The natural flow of blood may be hampered as a result of this.
You are not too young to be affected by high blood pressure, even if you are a young adult. Even though they appear to be healthy, about 50% of individuals over the age of twenty have raised or high blood pressure. Although high blood pressure has no evident symptoms, it should not be overlooked.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure often has no visible indications or symptoms, hence the American Heart Association refers to it as ‘the silent killer’. Some patients have stated that they experience:
- Persistent headaches, often severe
- Nosebleeds
- Tiredness
- Blurry vision or other issues with vision
- Pain in the chest
- Breathing problems
- Irregular heartbeat
- Urine with blood
These symptoms aren’t specific, and they usually don’t show up until a patient’s blood pressure has reached severe or life-threatening levels.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
There are two sorts of high blood pressure causes. Primary hypertension develops over time and without a clear reason. Underlying disorders such as sleep apnea, kidney issues, and adrenal gland tumors create secondary kinds.
Furthermore, there are some risk factors to consider, including:
- Age
- Race
- Family Background
- Weight
- Level of Physical Activity
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- High-sodium diet
- Stress
How to Combat High Blood Pressure
Lowering your blood pressure isn’t as difficult as you might believe.
- If you’re a smoker, you’ll have to quit.
- Keeping a healthy body weight. If you’re overweight, even a 10 pound weight decrease can help lower your blood pressure.
- Salt consumption is kept to a minimum. Limit your daily salt intake to 1,500 mg.
- Getting enough exercise is essential. Every week, try to workout for at least 90 minutes.
- Keeping alcohol to a minimum. Limit yourself to one glass a day at max.
- Eating well is important. Aim for a low-saturated-fat and high-fiber diet, rich in fruits and vegetables.
Enroll in a Prescription Assistance Program
Now that you know how common hypertension or high blood pressure is, even for young people, you need to be prepared in case if get diagnosed with it in the future. Enroll in The RX Helper’s prescription assistance program, which allows underinsured or uninsured Americans to get affordable medication programs at highly subsidized rates or completely free of cost.
Contact us now to learn more, or click here to enroll in our prescription assistance program.