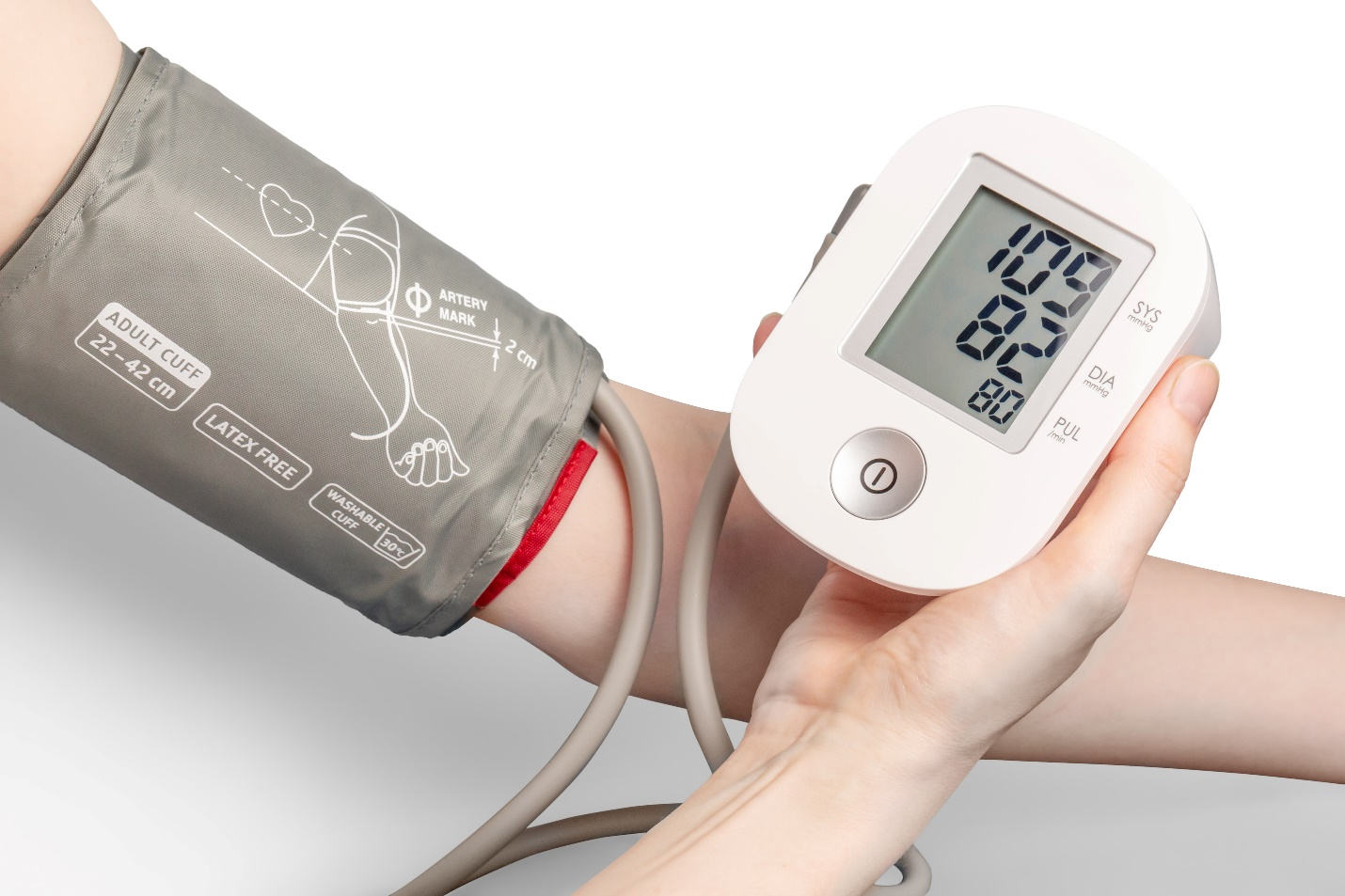
Hypertension is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases to affect people all over the world. Currently, it affects about 1.3 billion people worldwide and kills about 10 million people every year.
While lifestyle changes are often recommended to control it, medical intervention becomes imperative at some point. Hence, determining the safety and efficacy of existing interventions is only justified. In this debate of calcium channels vs. beta blockers, we will help you determine how the two compare in their approach to treating hypertension.
How Do Calcium Channel Blockers Work?
Calcium Channel Blockers, or CCBs, work by dilating the arteries. As a result, the heart is able to pump blood easily, reducing its need for oxygen. Apart from hypertension, CCBs also help treat cardiomyopathy, rapid heart rhythms, and angina.
How Do Beta Blockers Work?
Beta-blockers work by blocking the neurotransmitters from binding to beta receptors on nerves. The two neurotransmitters they block are norepinephrine and epinephrine. As a result of dilated blood vessels, the blood pressure and heart rate are significantly reduced.
Just like CCBs, beta blockers are used to treat angina, high blood pressure, and heart failure. Furthermore, they can also prevent future heart attacks if one attack has already taken place.
Calcium Channels Vs. Beta Blockers: What Are the Side Effects?

Side Effects of Beta Blockers
Here are some of the most common side effects of beta-blockers:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Vomiting
The less common side effects include:
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Blurred Vision
- Disorientation
- Muscle cramps
- Rash
While they reduce blood pressure and slow heart rate, they can also cause heart block or heart failure in patients with heart problems.
Furthermore, sudden withdrawal may also worsen chest pain and lead to abnormal heart rhythms. In people with diabetes, they may also cause high or low blood glucose.
Side Effects of Calcium Channel Blockers
Some of the most common CCB side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Rash
- Headache
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Low Blood Pressure
- Edema
However, side effects are not the only criteria to consider when choosing the right drug. Factors such as medical expenses and evaluation of existing medical conditions also come into play.
Interaction of CCBs With Other Drugs
The CCBs mostly interact with diltiazem (Cardizem) and verapamil (Calan, Isoptin). This is mainly because these two reduce the elimination of many drugs by the liver.
Interaction of Beta Blockers With Other Drugs
Beta-blockers also interact with a range of drugs. However, some interactions may result in adverse effects. For example, if a beta blocker is combined with clonidine (Catapres), it may cause heightened blood pressure.
Final Word
In a nutshell, both drugs help treat hypertension by dilating blood vessels. In some cases, the “calcium channel vs. beta blockers” debate may not be enough to deduce which approach is better. It’s also important to have a careful assessment of symptoms and existing medical conditions done.
Only after a detailed evaluation of your condition can you start using the prescribed drug. So, if you’re underinsured or uninsured and require prescription assistance for medications, get in touch with us right away. At the Rx Helper, we help you get the medicines you need for little or no money.